This article provides best practices and naming conventions for data modeling.
Naming Conventions
xMart tables and fields have CODE, TITLE and DESCRIPTION properties. xMart naming conventions only pertain to the CODE property. The CODE becomes the physical name of the table or field as stored in the database or exposed via API or as seen in tools such as Power BI. There are no conventions for the TITLE or DESCRIPTION properties.
Table and Field CODEs
Once a data mart goes “live”, table and field codes are effectively permanent. For both table and field CODE values.
- All uppercase letters or numbers.
- No spaces or punctuation other than “_”, “-“, “.”
- Keep short
- Use an underscore character to separate the words/segments of the code (ie CASES_BY_AGE)
Table CODEs
The first word/segment of a table CODE should indicate the type of table and is used by the user interface to organize the tables:
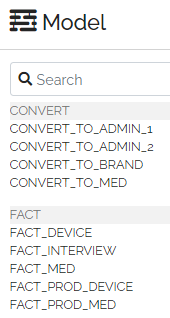
Try to use one of the following “standard” prefixes:
| Prefix | Table type | Example |
|---|---|---|
| REF | Reference/master data | REF_COUNTRY |
| FACT | Fact/observation data | FACT_CASES |
| RAW | Raw, extracted data prior to transformation | RAW_2018_EXCEL |
| CONVERT | Code conversion table | CONVERT_TO_ISO3 |
Make up your own prefixes as needed.
Field CODEs
Follow a NOUN_ADJECTIVE pattern
Instead of naming fields like FIRST_NAME and LAST_NAME, use NAME_FIRST and NAME_LAST.
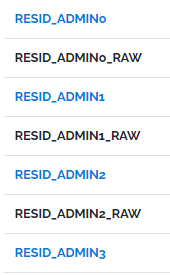
One practical advantage of this is that because most tools sort fields alphabetically, related fields will be displayed next to each other. Another big advantage is that it makes it easy for a person to find all of the fields about a certain thing with just a quick glance.
A set of fields from case-based data about an individual’s residence. It is obvious that this set of fields all describe the residence.
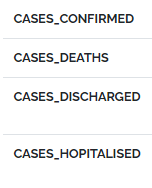
CASES_CONFIRMED rather than CONFIRMED_CASES
This has 2 main advantages :
- All of the data on a subject appears together alphabetically.
- Always using the same pattern makes remembering column names easier.
Date
It can be useful to use DATE as a prefix in datasets where date is the most important concept
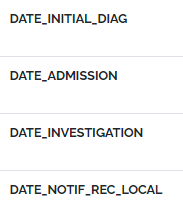
Define and use consistent abbreviations
Because field names become column headers in excel spreadsheets, etc. it is best to keep them relatively short while also being descriptive, a tradeoff.
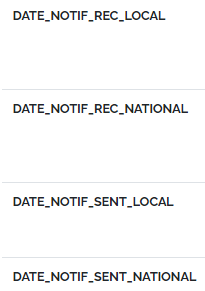
One tip to striking a balance between these two extremes is to define and use consistent abbreviations for repeated long text.
For example, a table has a lot of fields about when notifications have been sent and received. Instead of writing out “NOTIFICATION” everywhere, it was abbreviated as “NOTIF”. Likewise “RECEIVED” is abbreviated as “REC” These can then be combined to create short but still descriptive field names.
Best Practices: REF Tables (reference data)
In most cases, reference data can be put into tables like this
| Code | Title | Type | Mandatory | BPK | RowTitle | Contains |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CODE | Code | TEXT_10 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Human Readable Code for the reference |
| TITLE | Title | TEXT_50 | Yes | No | No | Name to display |
| DESCRIPTION | Description | TEXT_450 | No | No | No | Longer textual description of the record |
But a lot of cases translations for the data are available. In which case the best option is
| Code | Title | Type | Mandatory | BPK | RowTitle | Contains |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CODE | Code | TEXT_10 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Human Readable Code for the reference |
| TITLE_EN | Title (English) | TEXT_50 | Yes | No | No | English name to display |
| TITLE_FR | Title (French) | TEXT_50 | No | No | No | French name to display |
| TITLE_ES | Title (Spanish) | TEXT_50 | No | No | No | Spanish name to display |
| TITLE_AR | Title (Arabic) | TEXT_50 | No | No | No | Arabic name to display |
| TITLE_ZH | Title (Chinese) | TEXT_50 | No | No | No | Chinese name to display |
| TITLE_RU | Title (Russian) | TEXT_50 | No | No | No | Russian name to display |
| DESCRIPTION | Description | TEXT_450 | No | No | No | Longer textual description of the record |
This can be made into a view to make a long format like this in SQL
SELECT
CODE,
'EN' AS LANG,
TITLE_EN AS TITLE
FROM
mart.REF_TABLE WITH (NOLOCK)
UNION
SELECT
CODE,
'FR' AS LANG,
TITLE_FR
FROM
mart.REF_TABLE WITH (NOLOCK)
UNION
SELECT
CODE,
'ES' AS LANG,
TITLE_ES
FROM
mart.REF_TABLE WITH (NOLOCK)
UNION
SELECT
CODE,
'AR' AS LANG,
TITLE_AR
FROM
mart.REF_TABLE WITH (NOLOCK)
UNION
SELECT
CODE,
'ZH' AS LANG,
TITLE_ZH
FROM
mart.REF_TABLE WITH (NOLOCK)
UNION
SELECT
CODE,
'RU' AS LANG,
TITLE_RU
FROM
mart.REF_TABLE WITH (NOLOCK)
Or like this in a pipeline
<Extract>
<GetMart TableCode="REF_TABLE" OutputTableName="data" />
</Extract>
<Transform>
<UnpivotColumns>
<Column Name="TITLE_EN" ValuesToColumn="TITLE">
<Unpivot ToColumn="LANG" Value="EN" />
</Column>
<Column Name="TITLE_FR" ValuesToColumn="TITLE">
<Unpivot ToColumn="LANG" Value="FR" />
</Column>
<Column Name="TITLE_ES" ValuesToColumn="TITLE">
<Unpivot ToColumn="LANG" Value="ES" />
</Column>
<Column Name="TITLE_AR" ValuesToColumn="TITLE">
<Unpivot ToColumn="LANG" Value="AR" />
</Column>
<Column Name="TITLE_ZH" ValuesToColumn="TITLE">
<Unpivot ToColumn="LANG" Value="ZH" />
</Column>
<Column Name="TITLE_RU" ValuesToColumn="TITLE">
<Unpivot ToColumn="LANG" Value="RU" />
</Column>
</UnpivotColumns>
</Transform>
Best Practices: Standard REF Tables
When you create a new mart, it is good to use some standard reference data. There is a lot of it in REFMART where you can download the table structure and put it into your own mart.
If you set up a simple pipeline, you can keep the data up to date automatically
<XmartPipeline IsDbOnly="true">
<Extract>
<GetMart MartCode="REFMART" TableCode="REF_COUNTRY" OutputTableName="ref_country" />
</Extract>
<Transform>
</Transform>
<Load>
<LoadTable SourceTable="ref_country" TargetTable="REF_COUNTRY" LoadStrategy="MERGE">
<ColumnMappings Auto="true" />
</LoadTable>
</Load>
</XmartPipeline>
REF_COUNTRY is useful to have because you will normally need at least one Foreign Key to it. There are other reference tables available in REFMART which you can use in Views so you don’t need to copy the data, you just need tpo create a custom view to them.
Some useful tables are
-
REF_DATES Has the dates with the Week, month and year for ISO, EPI and MMWR as well as the quarter and the day of the year.
-
REF_POPULATIONS Has the population figures by country, sex and agegroup going back to 1950 and projected forward to 2100.
Best Practices: FACT Tables
Ideally, a Fact table should contain Reference data and Facts only. There should be a BPK on it to make data faster to load and read as well as enabling the table to be updated.
Whereas in a standard database Primary Keys are mandatory, xMart allows them to be set up as optional.
They are displayed like this with a Key in the Is Key field to indicate that the field is in the BPK and a red star next to the field code to indicate that it is mandatory
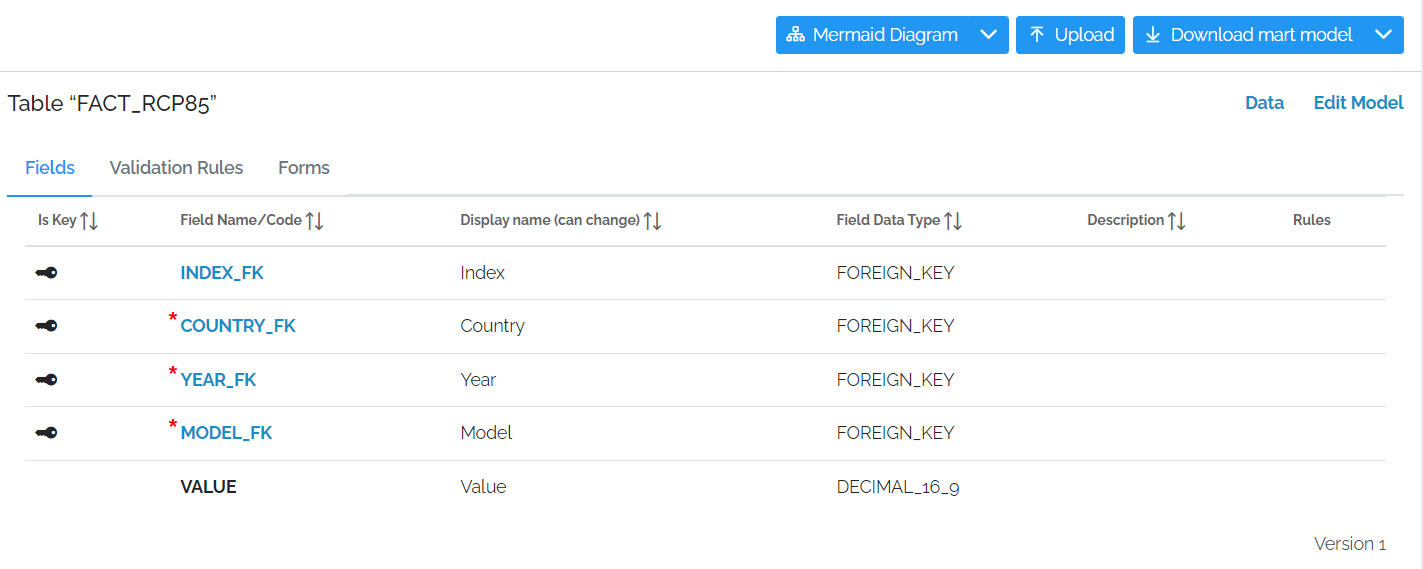
In this image, the first four fields are the BPK but INDEX_FK is not mandatory. The table also only contains the Foreign Keys for the Reference data and a Fact column which is value.
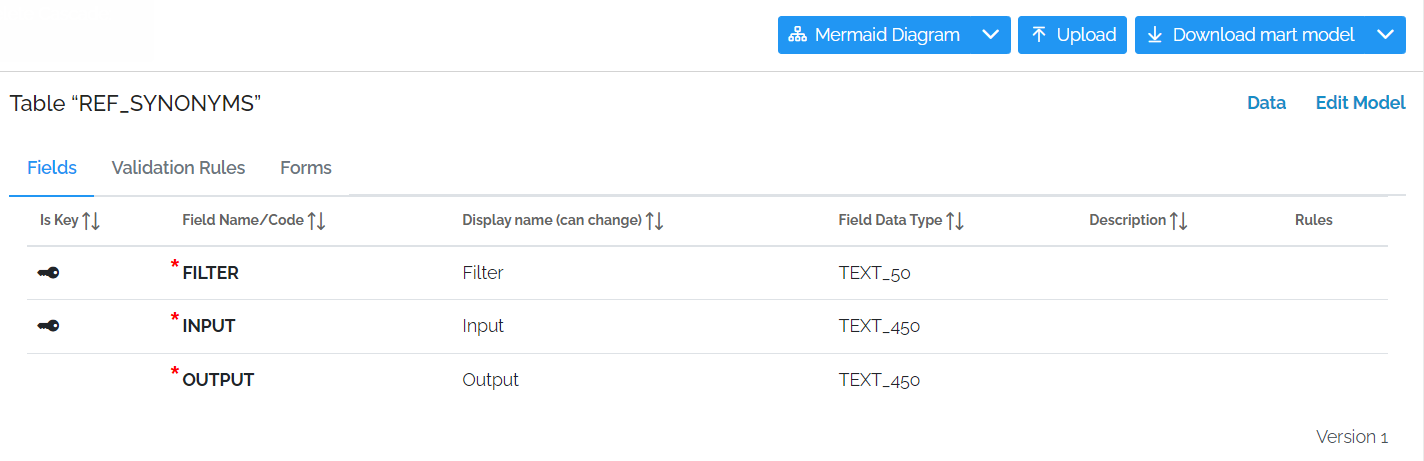
Best Practices: SYNONYM Tables
Synonym tables require, at the very least, an input column and an output column. In order to be able to use the same Synonym table for many different lookups, it is a good idea to add a filter column as well in case a value needs to be translated in different ways for different columns.